



The resourceful farmers’ knowledge of the earth is harmonious with the responsibility to be good stewards of this wonderful gift from God: our planet.
In 2018, Agros initiated a process for applying the Rick Steves Climate Smart Commitment as a cross-cutting methodology at all its agricultural programs in Central America, in line with its mission to creating sustainable and resilient communities, transform the livelihoods of farming families and build for them a brighter future.
Increasing farmer’s resilience and adaptive capacity.
Reducing agriculture’s carbon footprint and making agriculture part of the solution.
Ensuring farmer’s livelihood are not threatened by mitigation and adaptation efforts: practices must benefit farming families.

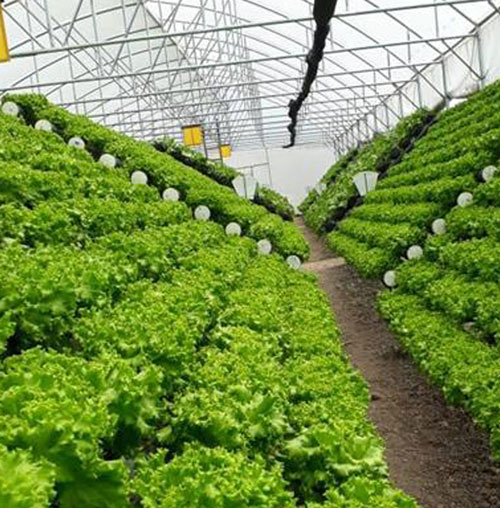
In response to the global challenges posed by climate change, the organization has focused on enhancing the resilience of the production systems. Oneway to achieve the adaptation of Agros’ farming program, is the farmers development of a strategic crop rotation of vegetables breaking the cycles of pests and diseases. When farmers have knowledge of practices that build healthy ecosystems, their ability to adapt becomes greater, and their communities and supply chains benefit.
For instance, in the coffee plantations located in Nicaragua we promote the cultivation of grafted coffee plants where the roots are Robusta, a drought-resistant variety, and the floral graft is a high-quality Arabica variety. This innovative approach helps farmers better withstand water scarcity and ensures a consistent and high-quality coffee yield.

Agros is dedicated to reducing the environmental impact of agricultural activities. Its initiatives include the creation of terraces and planting of forests that help negate soil erosion, protect vital water sources, and the installation and implementation of biofactories for producing agroecological bio-inputs in regular manner, therefor minimizing the use of fossil fertilizers.
These actions help offset carbon emissions and contribute to a healthier planet, while also enhancing the sustainability of farming practices.


Integration of technology, increase of productivity, and proper water resource management.
To integrate these three climate-smart principles, Agros embarked on a comprehensive learning journey. Initially, to trained the staff in Best Agricultural Practices (BAP), enabling them to develop a robust training curriculum for beneficiary producers and their families. This ongoing process evolves continuously within each area of impact of Agros programs in Central America.

In conjunction with the continuous training in BAP, the organization made strategic investments to sustainably adapt the production system from social, economic, and environmental perspectives. This effort led to the development of Climate Smart Agribusiness Modules, encompassing:
These areas enable year-round crop production, beyond seasonal limitations. They provide better pest and disease control and facilitate the responsible use of water resources.
By introducing economically valuable species, such as fruit trees, the producers are self-encouraged to protect them. These trees capture carbon, and release oxygen, acting as regulator of the temperature. The nursery, producing reforestation species, also safeguards water sources by enclosing areas with recharge zones.
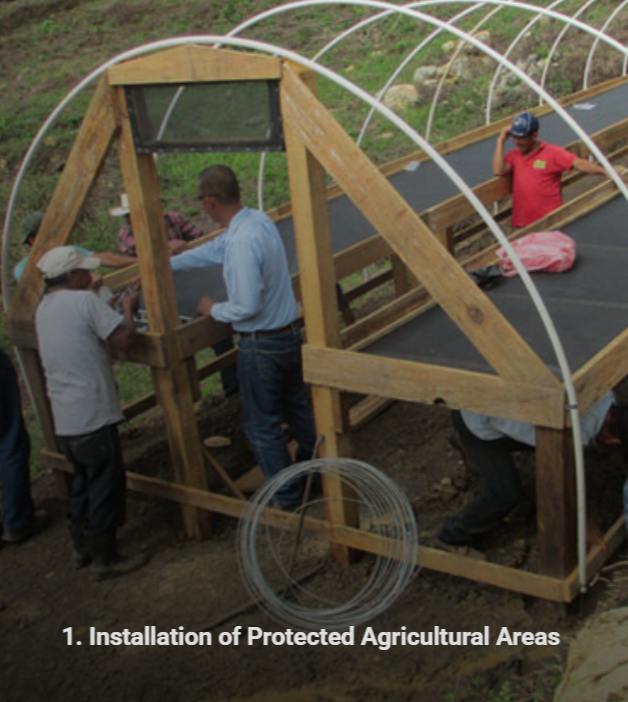

These areas enable year-round crop production, beyond seasonal limitations. They provide better pest and disease control and facilitate the responsible use of water resources.

By introducing economically valuable species, such as fruit trees, the producers are self-encouraged to protect them. These trees capture carbon, and release oxygen, acting as regulator of the temperature. The nursery, producing reforestation species, also safeguards water sources by enclosing areas with recharge zones.

The installed biofactories develop fertilizers from local resources to create biopesticides and utilize microbiological agents. Annually, Agros biofactories produces: 220 tons of biofertilizers The biofactory process involves harvesting of microrganisms from mountainous areas that have remained uncultivated for at least 10 years, or never cultivated at all. We collect the top 10 cm of decomposing leaves, which are placed in fabric bags along with molasses, semolina, and flours to multiply microorganisms. Depending on the ingredients, microorganisms reproduce aerobically or anaerobically, altering the fermentation level and transforming the mixture into 100% organic liquid fertilizers, root promoters or nematicides.
Agros’ mission is to transform lives through the development of prosperous agrovillages.
Therefore, investment in training modules, Agros houses, and biofactories transcends the concept of climate-smart agriculture, into building climate-smart villages where residents adopt the following processes:
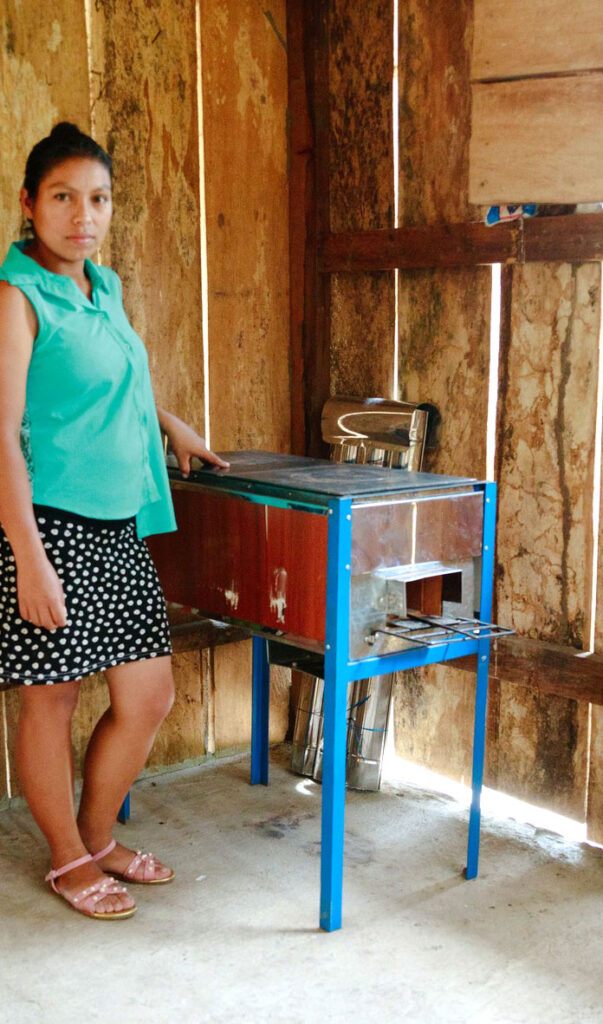

The eco-stoves replace fire pits, reducing household firewood consumption by 50% to 70%, which equates to five to eight trees per family per year. At the same time, this system is supported by the development of energy plantations aimed at producing the firewood each family needs for cooking, thereby preventing environmental depredation.
Before: require large amounts of firewood, poor ventilation exposing households to highly toxic, dense smoke.
After: The fire’s isolation in combination with better air flow, makes the stove more efficient, requiring a smaller fire and less wood to thoroughly cook food.
The rational use of the resource, together with the protection of water sources or resources, guarantees clean and safe water for the families and abundant water for irrigation.
Before: the resource was scarce, families had to travel long distances to fetch water, the water did not meet ideal hygiene conditions, which had adverse effects on health, and the planting periods and yields were subject to the behavior of the rainy season.
After: the community has water resources year-round, which supports a full life in an agricultural community.
Families have flushing toilets connected to septic tanks, which ensures proper handling of excreta and prevents pit latrines from overflowing when it rains.
Before: during the rainy season, common pits would turn into flood flows that contaminated the community and increased the risk of unsanitary conditions.
After: By promoting hygienic practices, diseases are avoided. This effort is accompanied by awareness-raising efforts to ensure rational water use by resident families.
A recycling processes was installed, consisting of storing and collecting chemical residues for disposal treatment to ensure that these inputs do not reach rivers and other water sources to prevent them from becoming health hazards.
Before: Community members used containers contaminated with chemical residues as household utensils or for agricultural production.
After: In every alley and street of the Agros Aldeas, a disposal bin has been established for proper chemical waste disposal.
The Agros Aldeas counts with garbage bins in common areas to provide the community with a waste disposal system. This effort is accompanied by a continuous awareness process for properly reclying household waste.
Before: Villagers would burn the garbage in open fields, exposing people to pollutant particles that endanger their health and affect the environment of the community.
Now: Families properly dispose of their waste in bins, which the municipal cleaning system transports to landfill areas.
Increase in crop yields:
18-32%
(depending on the crop)
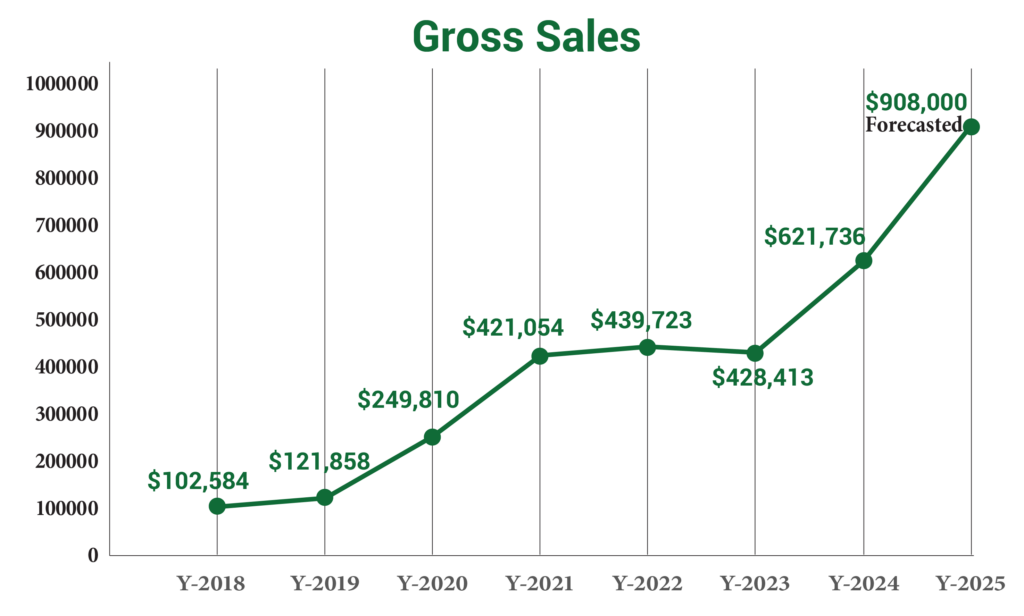
The application of the CLIMATE SMART PRINCIPLES is not carried out in a controlled lab plot or pilot project but is implemented in a scalable model with all program producers.




By adopting Climate Smart Principles and developing Climate Smart Villages, Agros’ programs benefit us all by helping reduce the impacts of climate change.
Agros is evaluating its production systems to determine their capacity as a carbon emitter or carbon capture system on a regular basis, by using Cool Farm Tool (CFT), the most recognized methodology for measuring emissions and carbon capture.
Having established a track record of exceptional impact, Agros is now ready to go broader and deeper. We are transforming entire regions by fully integrating our farmers into high-value markets, and by implementing productive modern infrastructure, successful social programs, and climate smart farming practices.
When you invest in AGROS, you are investing in an agricultural system that not only reduces its carbon footprint but also has a holistic impact on families:
Join us in our mission to create a sustainable and prosperous future for all.
HERE IS HOW YOU CAN HELP: